RNA polymerase moves along the template strand synthesising an mRNA molecule. Eventually when the RNA polymerase is done its job it will.
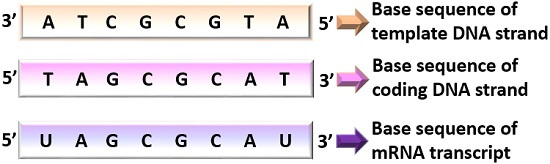
Difference Between Template And Coding Strand With Comparison Chart Biology Reader
DNA synthesis occurs on both strands in the directions away form the origin of replication which generates a replication bubble.
The template strand of dna. In prokaryotes RNA polymerase is a holoenzyme consisting of a number of subunits including a sigma factor. More importantly what is unique about RNA polymerase is that it works with the nucleotides A G C and U- NOT T. B It serves as the start point for the new DNA strand.
A DNA template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme DNA polymerases and RNA polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of DNA or at the time of transcription of RNA respectively. The terms template strand sense strand and coding strand are commonly used to describe one of the two strands of DNA however the nomenclature is quite confusing because different authors have used these terms to describe both strands -- one school argues that the strand copied into mRNA should be considered the template strand but the other school argues that the opposite strand which. A It serves as a guide in determining the next nucleotide to be added according to the Watson-Crick base pairing scheme.
So C T T a C a C C C C T G a C T T c G C G CCG and T. Directional polarity and function. Hence the directionality of the template strand should be 3 to 5.
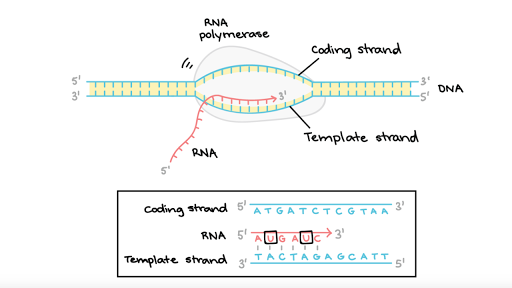
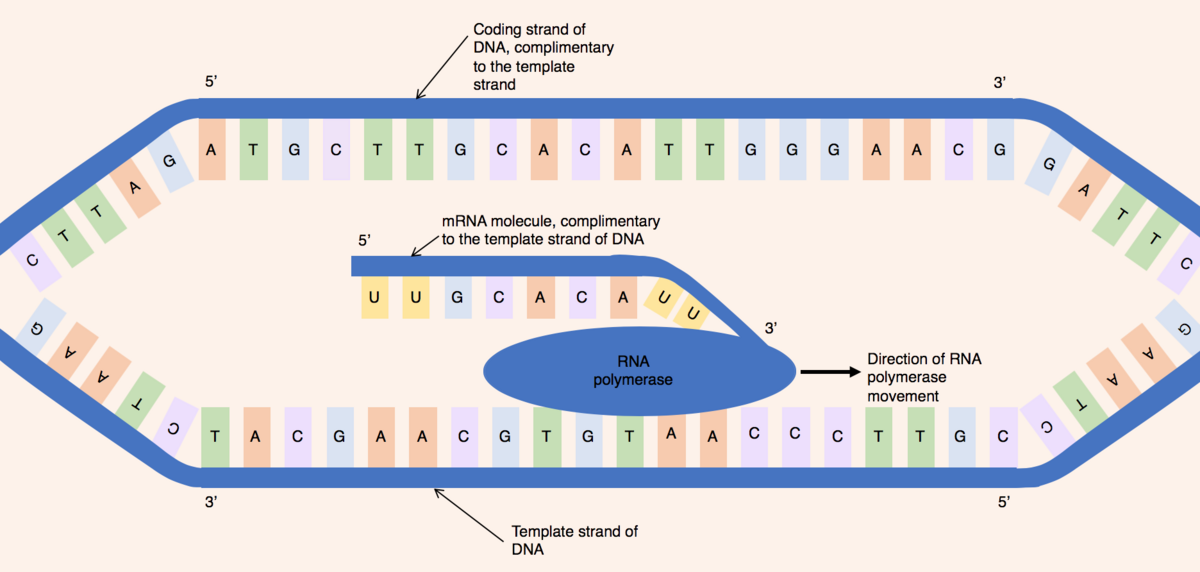
Because of their molecular structures A and T nucleotides always pair with one another and C and G nucleotides. DNA Template strand therefore is the term that refers to the strand used by DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase to attach complementary bases during DNA replication or RNA transcription respectively either molecule moves down the strand in the 3 to 5 direction and at each subsequent base it adds the complementary of the current DNA base to the growing nucleic acid strand which is thus. RNA polymerase copies the template strand of DNA making single-stranded mRNA complementary to the DNA template.
C It allows the DNA polymerase to move along it easily. Asked Jun 19 2017 in Chemistry by sosocat. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules with each newly formed double helix containing one new and one old strand.
Answered Jun 18 2020 by denacht. Asked Jun 18 2020 in Anatomy Physiology by jayjay. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Using the DNA as a template strand RNA polymerase builds a new RNA molecule through base pairing and this process is generally called elongation. So with this template strand it is written from a five prime 23 prime orientation. Looking forward to quarter break so I dont.
The template strand serves as the DNA template for transcription which is the first step of gene expression. The RNA polymerase does this by moving in the 5 to 3 direction. A template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase to attach complementary bases during DNA replication or RNA transcription respectively.
The difference between template and coding strand is mainly due to the following properties. The DNA molecule unwinds and separates to form a small open complex. Although RNA polymerase traverses the template strand from 3 5 the coding non-template.
DNA sunthesis occurs at the replication forks in 5-3 direction and one strand will be synthesized continously which is the leading strand and the lagging strand with be synthesized in small frag. Both template and coding strand are the two distinct strand of the double-stranded DNA in which the former works as a base to transcribe mRNA and the latter determines the correct base sequence of the mRNA. During transcription the RNA polymerase read the template DNA strand in the 35 direction but the mRNA is formed in the 5 to 3 direction.
The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5 to 3 direction. Strands and Directions of Synthesis. The new end is.
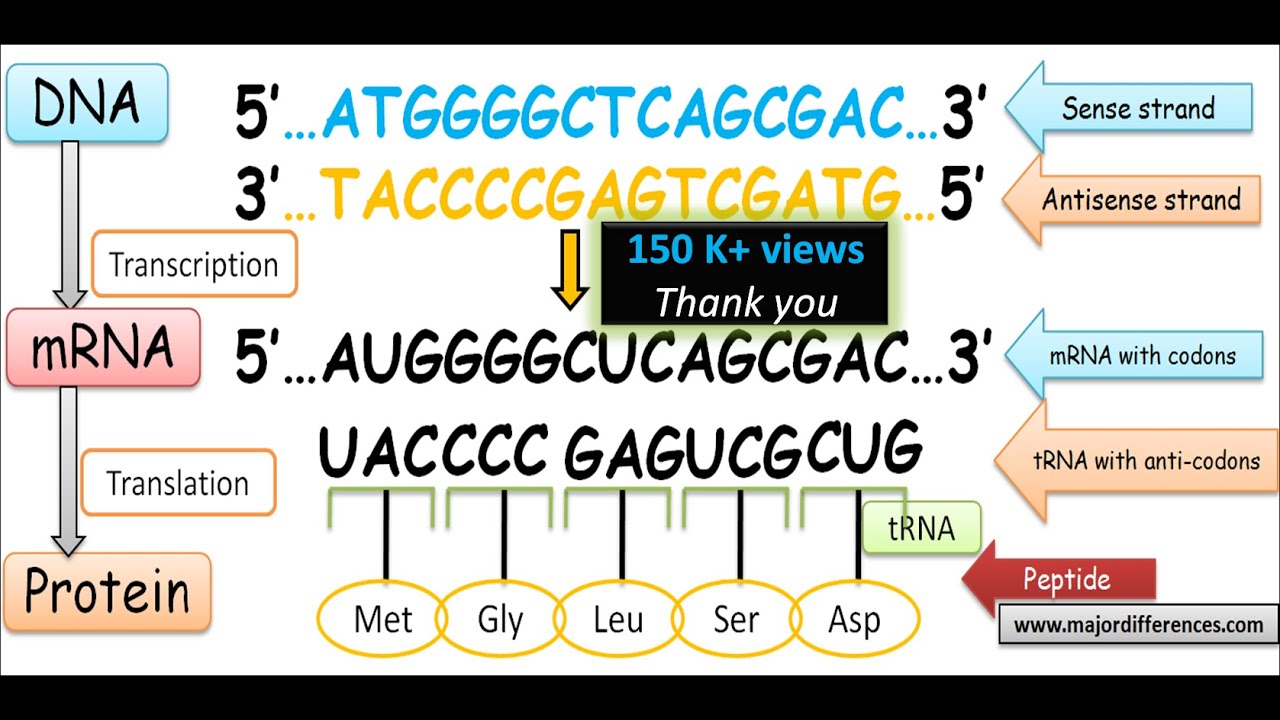
All strands are synthesized from the 5 ends to the 3 ends for both DNA and RNA. Key Difference Template vs Coding Strand In many organisms DNA acts as the information store while RNA acts as the messenger. Template DNA strands have portions called exons which code for proteins and portions called introns that do not contain code for proteins.
RNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to form the primary RNA transcript. In Molecular Biology the template strand is that one of the two in a double-stranded coding DNA that is used to direct the synthesis of an RNA molecule during transcription. Either molecule moves down the strand in the 3 to 5 direction and at each subsequent base it.
As transcription proceeds RNA polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create an RNA copy which elongates during the traversal. Were starting with the template strand of the DNA. So Im going to do that because it is going to be referring to the code ions off the.
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter of the template strand. What is the requirement for a template strand in DNA replication. Transcription in prokaryotes.
The old end is the cold end blue. As DNA polymerase makes its way down the unwound DNA strand it relies upon the pool of free-floating nucleotides surrounding the existing strand to build the new strand. The codons of the mRNA reading frame are translated in the 53 direction into amino acids by a ribosome to produce a polypeptide chain.
DNA replication is semiconservative meaning that each strand in the DNA double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. It is often useful to distinguish the two strands of DNA -- the strand that is copied into mRNA and subsequently translated has the mRNA complementary sequen. Protein chains are synthesized from the amino ends to the carboxy ends.
The nucleotides that make up the new strand are paired with partner nucleotides in the template strand. In such cases wither the molecule moves down towards the strand in the direction of 3 to 5. One strand of the DNA the template strand or noncoding strand is used as a template for RNA synthesis.
When the pre-mRNA is. The process of the synthesis of RNA from DNA is known as transcription which controls the gene expression and the production of proteins in many biological systemsIn this process two DNA strands are given specific names based on their. So first lets start by writing out the sequence.
She so you can notice that I wrote thes out in triplets. Answered Jun 18 2020 by morgangilfert.

Difference Between Sense Strand And Antisense Strand Of Dna Youtube
Solved 23 Transcribe The Following Sequence Of Dna Located Chegg Com

Dna Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Classifications Of Transcriptional Strand Bias A Rna Polymerase Uses Download Scientific Diagram
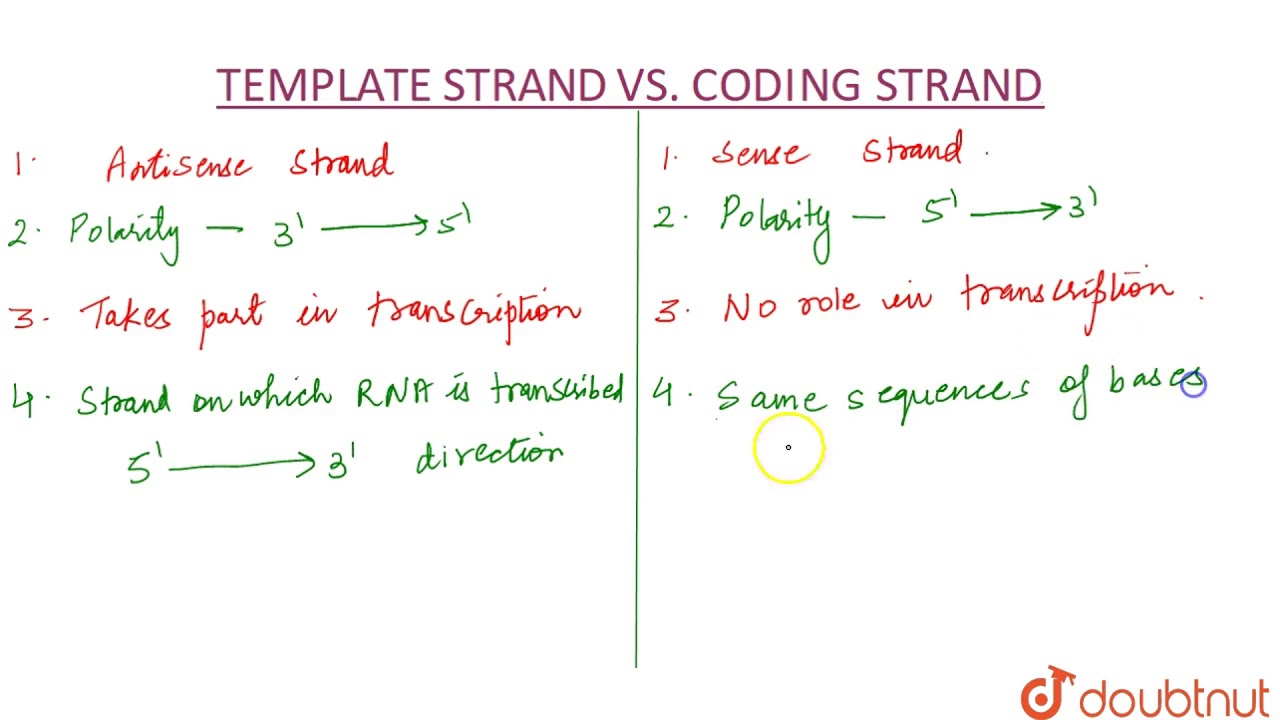
Difference Between Template Coding Strand Youtube
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
What Does It Mean To Say That Mrna Is Complementary To The Template Strand Of Dna Quora

Template Dna Definition Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Rosalind Glossary Template Strand
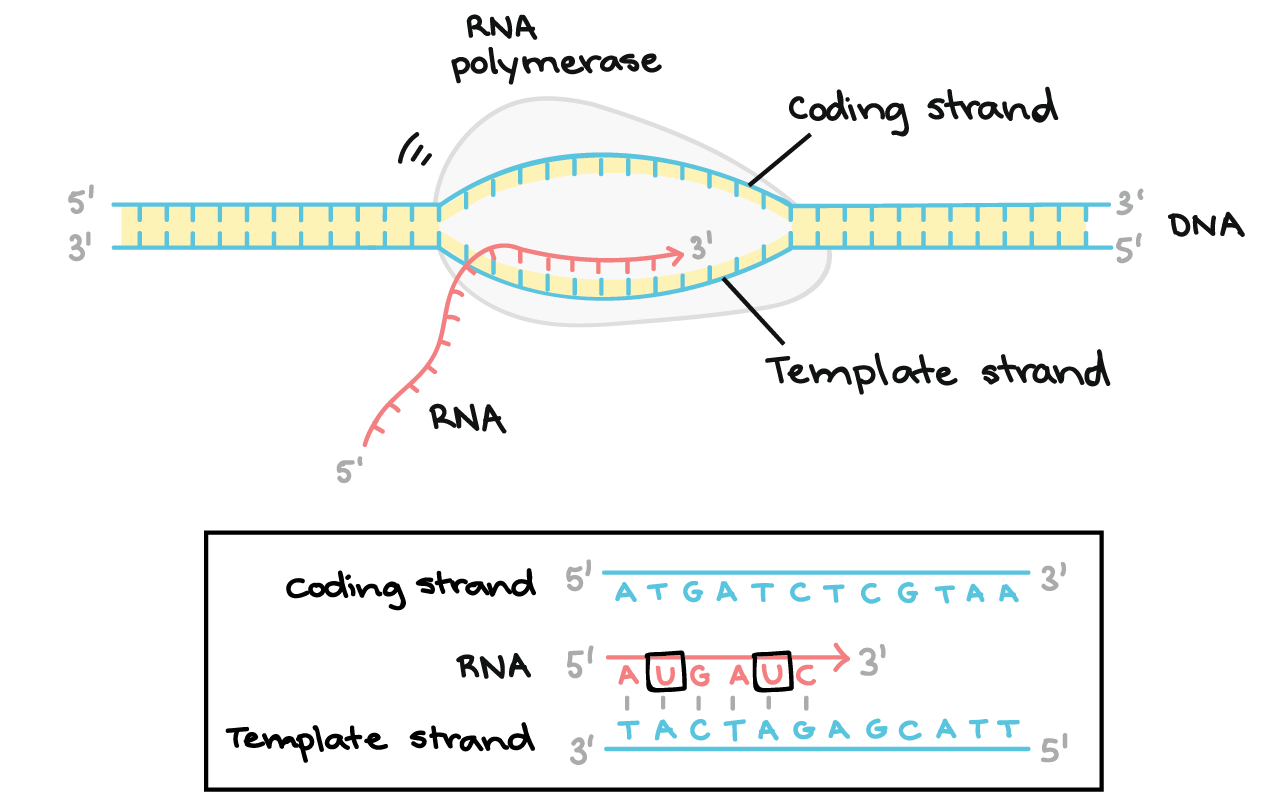
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy

How To Determine Which Strand Of Dna Is Transcribed Into Mrna Youtube
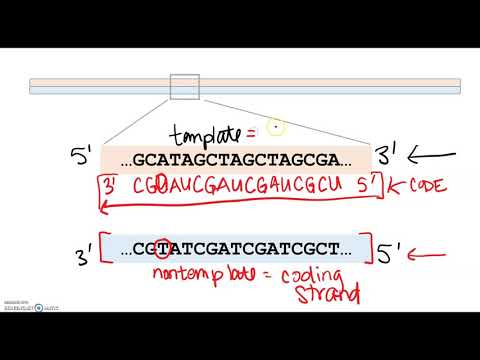
2 1 Overview Of Transcription Biology Libretexts
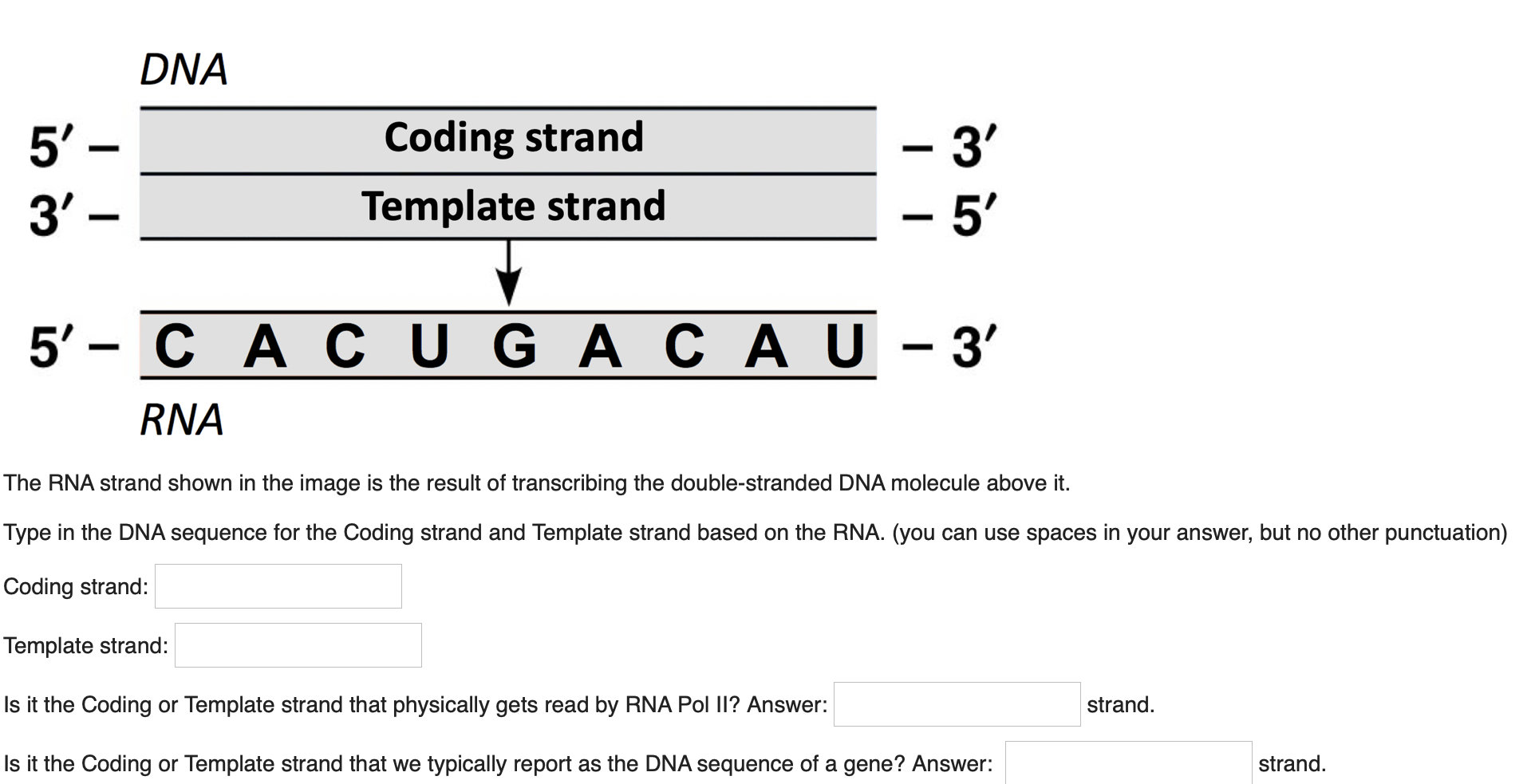
Solved Dna 5 3 Coding Strand Template Strand 3 5 Chegg Com
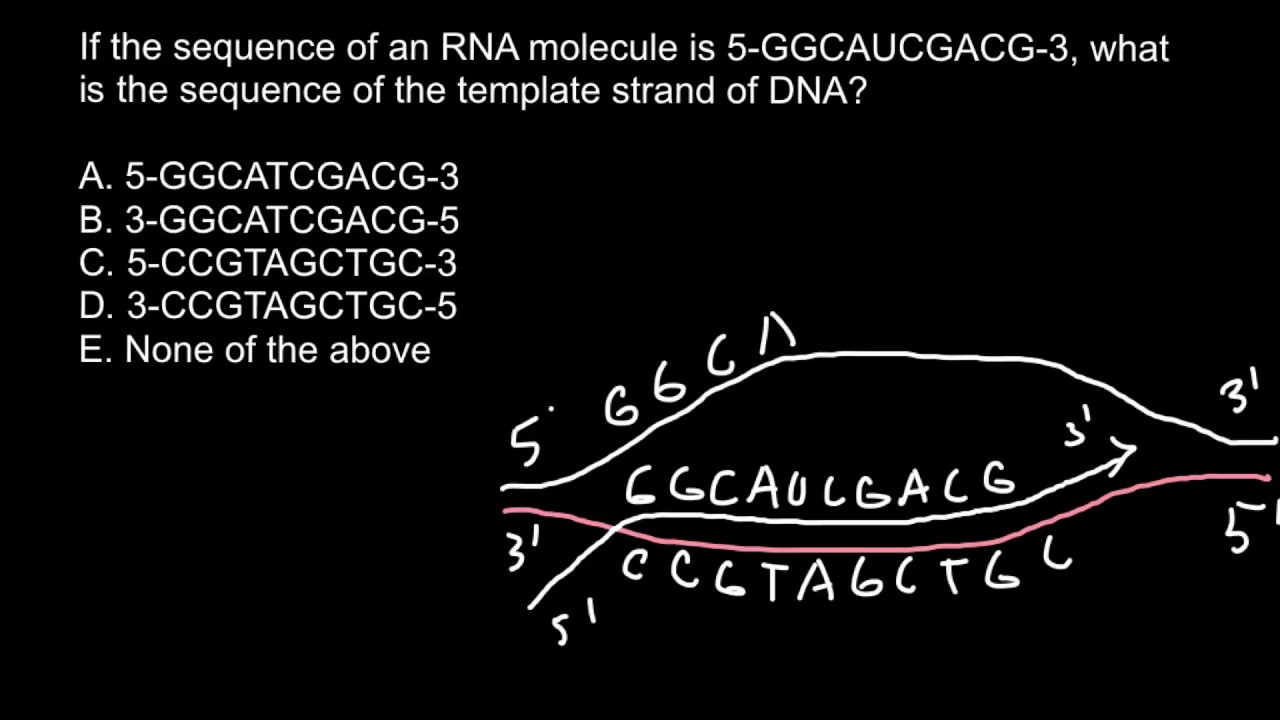
How To Find Sequence Of The Template Strand Of Dna Youtube
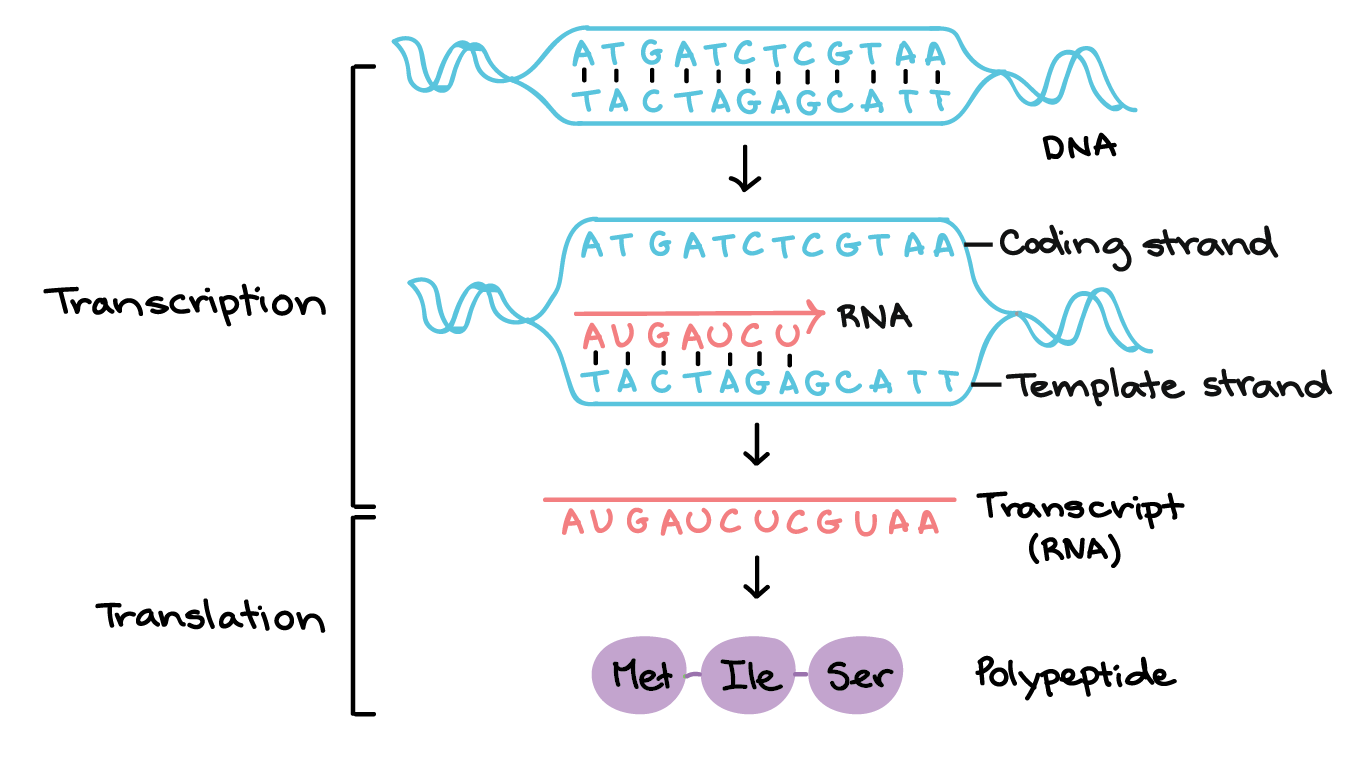
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy

Post a Comment
Post a Comment